In the year 2000, during the Millennium Summit in New York, global leaders convened to establish the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). The objectives were ambitious and focused on key areas of concern, particularly in regions like Africa, where poverty and underdevelopment were most acute. The MDGs highlighted critical issues such as maternal health, child mortality, poverty eradication, universal education, gender equality, disease eradication, and environmental sustainability.
Yet, despite the importance of these topics, one critical area was notably absent from the discussions: the role of statistics in achieving these objectives. There was no significant emphasis on the use of data as a tool for assessing progress, understanding challenges, and creating effective solutions. This article argues that the proper application of statistics would have accelerated Africa's progress towards these goals and continues to be a missing piece in the policy discussions of African leaders.
In light of this, we will explore six strategies-"Six Statistics HOWs"-to demonstrate how the effective use of statistics can solve Africa's most pressing problems, ranging from economic to environmental challenges. We aim to highlight the necessity of statistics as a vital tool for decision-making and development in Africa.
Table 1: Progress in Millennium Development Goals by Area of Focus
This table highlights the focus areas of the MDGs. However, statistical tools and analysis were underutilized in addressing these critical issues.
1. The Role of Statistics in Solving Africa's Problems
Statistics offer the most powerful means for understanding complex issues, tracking progress, and crafting actionable solutions. For Africa, where diverse challenges exist in sectors like healthcare, education, and the economy, data-driven approaches can produce meaningful change.
Key steps to utilizing statistics effectively include:
- Data Collection: Gathering accurate, high-quality data is the foundation of effective problem-solving. In Africa, innovative approaches such as mobile data collection in Kenya have improved the availability of real-time information, particularly in agriculture (Suri & Jack, 2016). Farmers are now using this data to optimize crop yields and improve food security
- Data Analysis: Advanced statistical techniques such as regression analysis, clustering, and machine learning can help uncover hidden patterns in the data. In Nigeria, fiscal policy outcomes have been improved through regression models, leading to more targeted economic decisions that address inflation (Central Bank of Nigeria, 2020).
- Data Interpretation: Interpreting data correctly is essential to ensuring that policies are effective. In South Africa, demographic data analysis has informed urban planning efforts, ensuring resources are allocated appropriately in rapidly changing urban environments (Stats SA, 2021). Misinterpreted data could result in misguided policies, emphasizing the need for expert analysis.
Figure 1: The Importance of Statistics in Addressing MDGs Focus Areas
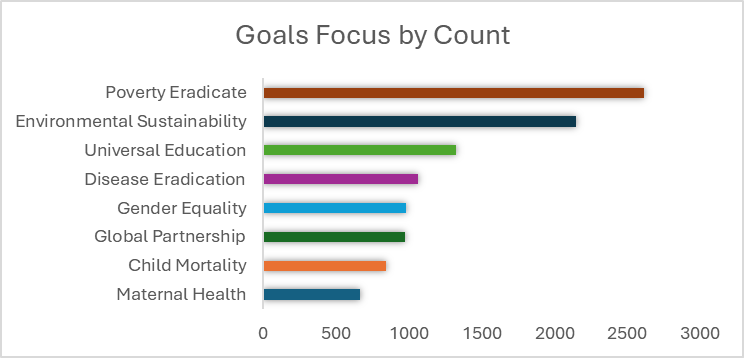
2. Improving Data Quality
The usefulness of data in solving Africa's challenges depends largely on its quality. Without accurate, consistent, and timely data, even the most well-intentioned policies can fail.
To improve data quality, it is essential to focus on:
· Accuracy: Ensuring data is precise and error-free is vital. In healthcare, accurate patient records are needed to predict disease outbreaks and implement appropriate interventions, such as managing the spread of malaria.
· Consistency: Maintaining uniform data collection across different regions and sectors allows for reliable comparisons. For example, Ethiopia's efforts to standardize agricultural data have allowed for better tracking of crop performance and improved food security initiatives (Ethiopian Agricultural Transformation Agency, 2019).
· Timeliness: Up-to-date data is necessary for effective decision-making. In Mozambique, the use of real-time weather data has helped manage climate risks in agriculture, enabling farmers to adapt to changing conditions swiftly (World Bank Group, 2018).
3. Enhancing Data Sources
Reliable data sources are critical to improving the quality and effectiveness of statistics. African countries need to diversify and standardize their data sources to ensure a holistic view of the challenges they face.
Key strategies include:
· Identifying Reliable Sources: Reputable sources, such as government agencies, international organizations, and research institutions, provide high-quality data. The World Bank's economic indicators, for example, serve as essential benchmarks for policy analysis in many African nations.
· Diversifying Sources: Relying on multiple data sources can enhance accuracy through cross-verification. In Uganda, combining satellite imagery with on-the-ground surveys has led to more accurate monitoring of deforestation rates, contributing to environmental sustainability (Global Forest Watch, 2020).
· Standardizing Collection Protocols: Implementing standardized data collection protocols ensures uniformity across various regions and sectors. In the East African Community (EAC), standardized trade data collection has improved economic planning and cross-border collaboration (East African Community, 2020).
4. Robust Database Management with Regulations
Improving the management of databases and ensuring strict regulations around data storage and usage are vital steps in ensuring data integrity and security.
Best practices include:
· Database Design: Databases must be structured efficiently to facilitate easy retrieval and analysis. In Rwanda, a well-designed health database has streamlined patient data management, improving healthcare delivery (Ministry of Health, Rwanda, 2020).
· Data Governance: Establishing clear rules around data access, management, and protection is crucial, particularly in sensitive sectors like finance and healthcare. Countries like Ghana have implemented strong data governance frameworks, ensuring that financial data remains secure and reliable (Bank of Ghana, 2019).
· Compliance with Standards: Ensuring compliance with global data privacy laws and management guidelines helps protect citizens' data rights. African nations can benefit from adopting European Union GDPR-like regulations to safeguard personal data, especially in the age of digitalization.
· Ethical Considerations in Data Use: Increased reliance on data for decision-making in Africa raises ethical concerns, particularly in politically sensitive areas. It is essential to adopt ethical frameworks that guide data collection, use, and privacy, ensuring that the rights of individuals are protected, and that data is used responsibly.
5. Leveraging Advanced Data Technologies
To maximize the potential of statistical data, African countries must invest in modern data technologies that streamline data management and enable real-time analysis.
Important technologies include:
· Database Management Systems (DBMS): Modern platforms like MySQL and PostgreSQL provide powerful tools for managing large-scale data efficiently. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these systems proved critical in managing vast amounts of health data across African nations.
· Data Backup and Recovery: Regular data backups and disaster recovery systems are essential to safeguard against data loss. In Ghana, a robust backup infrastructure has protected financial institutions from cyber-attacks and data breaches.
· Optimizing Database Performance: Efficient query optimization and load balancing can enhance database performance, which is critical for sectors like logistics and finance that rely on real-time data processing.
6. Investing in Trained Professionals
The success of data-driven solutions depends on the skills and expertise of trained professionals who can manage and interpret data effectively.
Key strategies include:
· Academic Training: African nations need to invest in higher education programs that focus on data science and statistics. Institutions like the African Institute for Mathematical Sciences (AIMS) are already leading the way by providing advanced training in these fields.
· Continuous Professional Development: Workshops, certifications, and industry conferences can ensure that data professionals stay updated with the latest tools and best practices. In South Africa, ongoing training programs are helping data scientists stay current with emerging technologies (AIMS, 2021).
· Practical Experience: Offering internships and hands-on projects helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application. Partnerships between universities and tech companies in Nigeria provide students with invaluable experience in data analysis (Nigerian Universities and Industry Collaboration, 2020).
Conclusion
Despite the extensive discussions during the Millennium Summit and subsequent global gatherings, the role of statistics has often been overlooked in addressing Africa's developmental challenges. By focusing on six key strategies-proper use of statistics, improving data quality, enhancing data sources, robust database management, leveraging data technologies, and investing in skilled professionals-African nations can harness the power of statistics to make informed decisions, optimize interventions, and achieve better outcomes across the continent.
If African leaders can place a stronger emphasis on statistical tools in policy-making and problem-solving, the continent stands a better chance of overcoming its most pressing challenges, from poverty to climate change.
Figure 2: Potential Impact of Statistical Interventions in Achieving MDGs
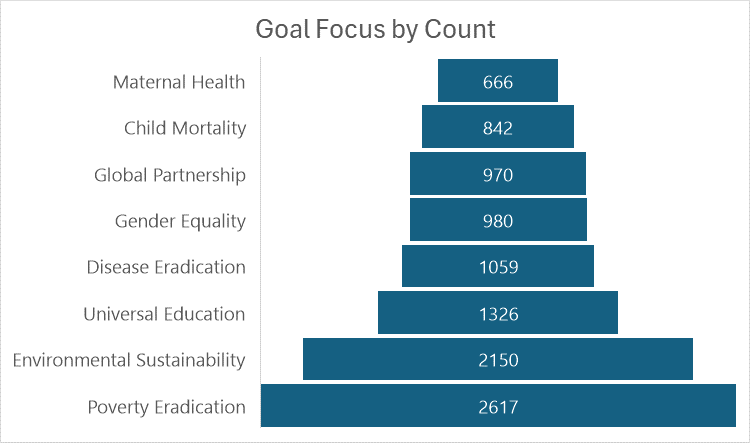
Dataset Details:
The data used in this analysis, sourced from the Millennium Development Goals dataset on Kaggle, highlights African countries' progress towards these goals. The dataset, last updated in 2016, provides valuable insights into the indicators related to education, healthcare, environment, and more, offering a snapshot of the challenges that continue to face the continent.
------------------------------
Lukmon Olayinka
Data Analyst
UnitedHealth Group
------------------------------